Dimensionality reduction is necessary in machine learning. We want to keep only the features that provide substantial information about our dataset.
The two aproaches are: „Feature selection” – It involves removing features that are not important to us. „Feature extraction” – It involves creating new, more complex features based on the existing base features.
Both examples will now be briefly discussed.
Feature selection involves searching for features that have low variance or have a lot of missing data. Variance is a measure of how much a certain quantity changes for the same type of measurement.

Example 1: We measure the diameters of apples and find that they have different sizes: 10cm, 6cm, 8cm, 8.5cm, 14cm. After checking, we discover that apples with a diameter of 10cm come from Brazil, those with 8cm come from Poland, and those with 14cm come from Spain. There is a significant difference in diameters, which indicates a large variance. Therefore, we can use diameter as a useful feature to classify apples.
Example 2: Apples have seeds inside. After measuring apples from Poland, Brazil, Spain, and other countries, we find that the length of seeds in each apple is quite similar. For example, seeds in Polish apples have an average length of 1cm with a standard deviation of 0.05cm, seeds in Spanish apples have an average length of 0.99cm with a standard deviation of 0.04cm, and seeds in Brazilian apples have an average length of 1.01cm with a standard deviation of 0.04cm. The variance, which is the extent to which the seed lengths differ among the countries, is very small. While this information is statistically significant, it may not be very useful for classifying apples.
Feature selection removes features with low variance, so it will remove the length of seeds and keep the diameter of apples. Let’s assume that our apples were described by 10 other features with low variance (similar to the seeds). Therefore, we had 12 features in total. Each feature used for apple classification contains information. Removing features with low variance results in a relatively small loss of information. The smaller the variance, the less information it contains.

Now, when we want to prepare our collected data (data collected by measuring the diameter of each apple, the length of seeds, and the other 10 remaining features), we need to have as few features as possible that will carry the most significant information. It turns out that after removing 11 features and keeping only the diameter of the apple, we retain 99% of the information needed for apple classification.
What we have gained:
- reduce the number of features – decrease the risk of overfitting
- lower complexity of the data
- less memory space used on the computer
- faster computations
In addition to these benefits, we have also eliminated concerns about falling into the curse of dimensionality.
Furthermore, let’s remind ourselves that the choice of features also depended on their availability in the measurements. If we had a feature that describes our apples well but is only available for 20% of the apples, we should remove that feature.
Feature extraction is the process of creating new features from existing ones. Here are some examples:
- Human has (height, weight). These are two features that increase the dimensionality by 2. We can cleverly compress these two features into one feature: BMI (Body Mass Index). This reduces the dimensionality of our data by 1. However, the disadvantage is having more abstract features.
- We measure features that have a lot in common. For example, measuring the lengths of fingers on a hand. If the data analysis is more focused on overall body proportions, we can simply use the average finger length, reducing the dimensionality by 9 dimensions.
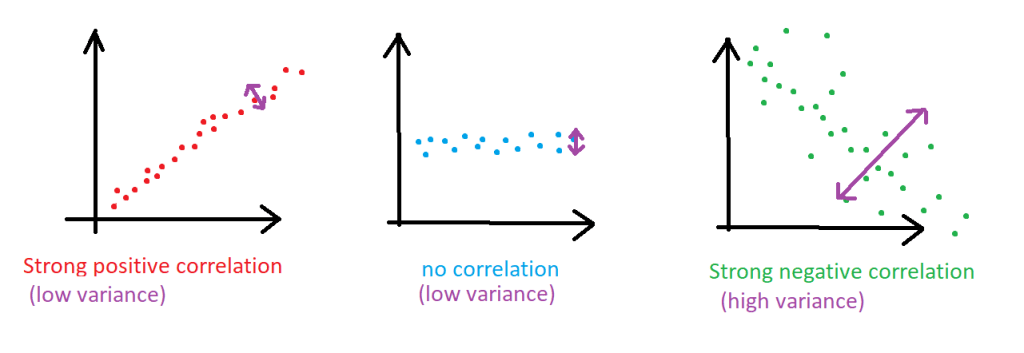
Correlation: It refers to the relationships between features. Correlation tells us which features are strongly related to each other. If there is a strong relationship, the correlation ‚r’ will be large (it can range from -1 to 1). A correlation close to -1 or 1 means that we can remove one of the features without a significant loss of information. For example, if the correlation between two features is -1, it indicates a perfect inverse correlation, which means removing one of the two features will not result in any loss of information.
I hope I helped you understand what dimensionality reduction is and what techniques are used in it.
Dodaj komentarz